Written by: Bryan Barron
Medically Reviewed by: Debra Jaliman MD Board-Certified Dermatologist
Updated on: 6/9/2025
In this article:
What is azelaic acid?
How azelaic acid works
Azelaic acid benefits
What is azelaic acid used for?
How to use azelaic acid
Is azelaic acid safe during pregnancy?
Does azelaic acid cause purging?
Can I use azelaic acid with salicylic acid?
Can I use azelaic acid with glycolic acid?
Can I use azelaic acid with vitamin C?
Can I use azelaic acid with retinol?
Can I use azelaic acid with benzoyl peroxide?
Can I use azelaic acid with niacinamide?
What should you not mix with azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid was once one of the best kept secrets in skin care, mostly known in medical and professional settings. Now it’s one of the more highly sought-after ingredients thanks to undeniable research demonstrating how it significantly diminishes the appearance of skin blemishes, helps fade post-acne marks and other discolorations, refines skin’s surface and even reduces sensitivity. In short, azelaic acid is an ingredient you need to know about.
Let’s dive into this powerhouse ingredient below.
What is azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid is a skin-friendly dicarboxylic acid with unique properties that can be derived from grains like barley, wheat and rye (1). However, the lab-engineered, synthetic form is typically used in skin care formulas because of its greater stability and effectiveness.
How azelaic acid works
Azelaic acid works by inhibiting misbehaving elements on and within skin's uppermost layers. Left unchecked, these troublemakers lead to persistent, visible skin imperfections (like brown patches and post-blemish marks), dull skin tone and signs of sensitivity (2). Essentially, azelaic acid has a radar-like ability to interrupt or inhibit what's causing skin to act up. Skin "hears" the message azelaic acid sends and responds favorably, which leads to skin that looks better, no matter your age, skin type, or concerns.
Azelaic acid benefits
Some of the research on azelaic acid has looked at prescription-only topical products with concentrations between 15% and 20%, but there are incredible skin benefits to be seen even at lower concentrations (3,4).
- Mild exfoliating action that helps unclog pores and refine skin's surface
- Skin tone-evening properties to help fade post-acne marks and other discolorations
- Significant skin-calming factors to reduce sensitivity and bumps
- Antioxidant power that contributes to healthier-looking skin
The research on the unique way azelaic acid improves skin led us to formulate our 10% Azelaic Acid Booster. The azelaic acid within targets a wide range of skin imperfections and is formulated with 0.5% salicylic acid for a bit of a pore-refining nudge. The 10% Azelaic Acid Booster also contains a soothing complex of brightening plant extracts plus skin-restoring adenosine, an energizing ingredient that visibly reduces signs of aging.
What is azelaic acid used for?
Azelaic acid’s many benefits lend themselves to a myriad of uses for skin. The ingredient is often touted as the perfect way to tackle an uneven tone or dark spots but this glosses over azelaic acid’s penchant for calming redness and smoothing skin.
Beyond the different skin concerns that this multitasking ingredient works on, azelaic acid can also be delivered through both prescription and OTC (over-the-counter) products, depending on the percentage included in the product, as we’ve mentioned above.
Now let’s get into what azelaic acid is used for.
Dark Spots
Reducing the appearance of dark spots and an uneven tone is azelaic acid’s top claim to fame and why it’s often compared to vitamin C. Azelaic acid conquers this concern by helping to interrupt an enzyme (tyrosinase) in skin's uppermost layers that would otherwise lead to uneven skin tone and dark spots (5).
Azelaic acid also helps reduce the appearance of dark spots that are incurred from previous inflammation, life changes, environmental damage and injury to skin (6,7).
Redness
Although it’s billed as a dark spot buster, azelaic acid is also routinely used to help soothe and calm the redness that’s often associated with irritation and sensitivity as well as being suitable for rosacea- and eczema-prone skin.
Although more research needs to be done to examine exactly how this acid does so, studies have already shown azelaic acid assists in the decrease of visible redness on skin, and is even suitable for rosacea-prone skin (8,9).
Skin texture
As a dicarboxylic acid, azelaic acid also has mild exfoliating properties. Through the usage of its keratolytic abilities, that is, the way that azelaic acid can break down the dead, dull outer layers of skin, it refines skin texture (10). Consistent usage of azelaic acid can result in fewer clogged pores and bumps as well as a radiant, healthy look.
How to use azelaic acid
Azelaic acid products “play” well with others, meaning you can layer it into your routine without worrying that the azelaic acid will overpower or deactivate other ingredients. If it’s an over-the-counter product, apply once or twice daily. If it’s prescription strength, follow the advice of your prescriber.
In the case of our 10% Azelaic Acid Booster, we recommend applying it after your normal cleansing, toning and exfoliating steps. It can be applied on its own or mixed into your favorite serum or non-SPF moisturizer. It's fine to apply it to the entire face, or you can target blemished areas as needed. During the day, finish with a broad-spectrum sunscreen rated SPF 30 or greater.
When to use azelaic acid
You can use azelaic acid as part of your morning or evening skin care routine–or even both!
Since azelaic acid is gentle on skin, when you use it is entirely up to your preferences and desired results. It is entirely safe to use up to twice a day.
How much azelaic acid to use
You don’t have to slather on a ton of azelaic acid to see results. In general, a pea-sized amount of an azelaic acid cream should be enough to cover the skin on your face in a thin, but effective, layer.
You can also use a thin layer of azelaic acid as a spot treatment on specific areas of your face, such as places prone to redness or discolorations.
Who should use azelaic acid and who should not?
Azelaic acid is a safe skin care ingredient that has widespread compatibility with all skin types and is typically well-tolerated, even by those with sensitive skin (11). Its multitasking abilities mean it’s sought after by those with varying skin concerns as well.
Who could benefit from azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid is particularly beneficial for those with blemished skin and/or those with uneven tone and bumpy texture due to the ingredient’s ability to help visibly reduce the appearance of dark spots and rough texture.
Those prone to redness and the discomfort of eczema can also reap the benefits of azelaic acid, since it can also be used to calm sensitivity. It’s even suitable for those struggling with rosacea.
Who should stay away from azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid is a widely applicable, safe skin care ingredient and agrees with many skin types. Adverse reactions and side effects to azelaic acid are not common, but as with any skin care ingredient, if you experience signs of irritation, stop use or experiment with applying less often (once every other day, for example).
Is azelaic acid safe during pregnancy?
Yes! The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists lists azelaic acid as one of the topical active ingredients (along with topical salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide and glycolic acid) it considers safe to use for breakouts during pregnancy (12).
How long does azelaic acid take to work?
Like other bioactive ingredients, you’ll see results from the first application of an azelaic acid product. A visible soothing of sensitivity is one of the benefits you’ll notice immediately. A more robust picture of azelaic acid’s benefits, like the visible reduction of dark spots and uneven tone, appear after one to three months of consistent usage. This assumes you’re also protecting your skin from UV light exposure by applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen rated SPF 30 or greater every day.
Does azelaic acid cause purging?
Although not widely known as a cause of skin purging, newer research suggests there are rare instances where this phenomenon occurs, especially if someone is using azelaic acid for the first time. Thankfully it’s a temporary issue, lasting about four-to-six weeks (one skin cell cycle). After purging skin soon does an about-face, looking remarkably better with ongoing use of this superstar ingredient.
Azelaic acid side effects
Azelaic acid is a fairly gentle skin care ingredient suitable for most skin types and tones. If you have reactive, sensitive skin or a compromised skin barrier, the application of an active ingredient (including azelaic acid) might cause dryness, flaking or irritation. That’s why it’s important to monitor how your skin responds to each new ingredient you incorporate into your routine.
Can I use azelaic acid with salicylic acid?
Yes, you can use azelaic acid and salicylic acid (AKA beta hydroxy acid or BHA) together to relieve redness, bumps, blemishes and clogs and to promote balance. In fact, layering the two can help promote healthy looking skin, especially for those with sensitive or acne-prone skin.
When used together, azelaic acid works on top of skin to accomplish its feats while salicylic acid works within skin, particularly within pores, to help remove clogs. The result? Even skin tone and texture with fewer blemishes.

Can I use azelaic acid with glycolic acid?
Glycolic acid and azelaic acid share similarities, but also some interesting differences. Although azelaic acid can exfoliate skin when properly formulated, it doesn’t exfoliate the same way or with the same level of effectiveness as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid.
So, can you use azelaic acid and glycolic acid together? Yes, in fact, this combination can be ideal for addressing the look of multiple skin concerns, from bumps to uneven skin tone to age-related concerns you may be struggling with (13).
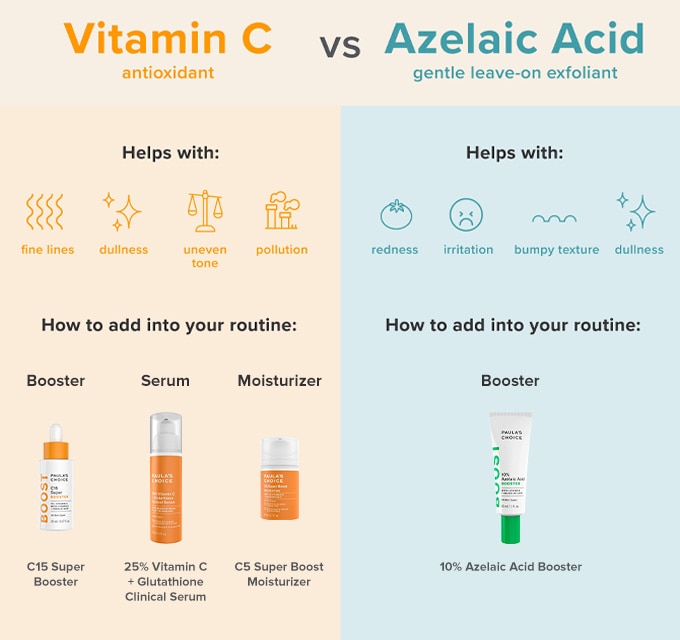
Can I use azelaic acid with vitamin C?
Yes, you can use vitamin C and azelaic acid products together. These ingredients complement one another; using them together may speed up the results for evening skin tone and fading marks by targeting the issue via multiple pathways.
Using azelaic acid and vitamin C together is as simple as seeking out a product formulated with both instrumental skin care ingredients or layering separate products with each ingredient over one another. Just remember, if mixing or layering these ingredients during the day, always round out your skin care routine with the application of a broad-spectrum SPF 30+.
Can I use azelaic acid with retinol?
Implementing both azelaic acid and retinol into your skin care routine is a safe and viable option, especially if you’re looking to tackle a mix of skin concerns, like anti-aging, uneven tone and bumps (14).
Like vitamin C and azelaic acid, you can look for a product that contains both ingredients or can layer products that contain each over one another.
Can I use azelaic acid with tretinoin?
You can use azelaic acid and tretinoin together, though it’s always a good idea to consult with your dermatologist first before laying and combining (15).
Listen to your skin! If the application of both ingredients simultaneously isn’t working for your skin, consider using one ingredient within your morning routine and another during your nighttime routine.
Can I use azelaic acid with benzoyl peroxide?
Research demonstrates that it is safe to use azelaic acid and benzoyl peroxide–in fact, this combination might just be what your skin needs to improve.
At least one study has found that using azelaic acid along with benzoyl peroxide boosts the effectiveness of azelaic acid, especially when it comes to tackling breakouts (15, 16).
Can I use azelaic acid with niacinamide?
You can definitely use azelaic acid with niacinamide as they’re two ingredients that respond positively to one another. Studies even find that niacinamide enhances azelaic acid’s ability to calm skin and fight dark spots (15)!
This combination of ingredients is best for oily, sensitive skin experiencing bumps or dark spots.
What should you not mix with azelaic acid?
Azelaic acid products can be used alongside many kinds of skin care products. There isn’t research showing it’s a problem to use alongside other powerhouse ingredients such as niacinamide and peptides. Of course, if you’re using a prescription version, consult with your physician on how to work it into your skin care routine.
Learn more about skin care ingredients.
Learn more about our editorial mission.
References for this information:
- Current Drug Therapy, June 2020, pages 181-193
- Indian Dermatology Online Journal, November-December 2020, pages 406-442
- Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, September 2015, pages 964-968
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, October 2016, pages 771-775
- Journal of Molecular Structure, January 2021, pages 129-234
- Pharmaceutics, April 2021, pages 567
- Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, September 2016, Issue 3, pages 269–282
- The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, March 2017, pages 37-40
- Experimental Dermatology, September 2010, pages 813-820
- Advanced Pharmaceutical Bulletin, June 2020, pages 239-246
- International Journal of Toxicology, July-August 2012, pages 5S-76S
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Website, Accessed May 2025
- Advanced Biomedical Research, February 2017, ePublication
- Journal of Drugs in Dermatology, April 2013, pages 434-437
- CosmoDerma, January 2025, pages 1-15
- Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, August 2000, pages S47-S50